How long can you run a CPU without a heatsink?
Are you curious about how long your CPU can survive without a heatsink? Well, we’ve got the answers for you! In this blog post, we’ll dive into the world of CPU cooling and explore the risks and limits of running a CPU without a heatsink.
The Role of a Heatsink in CPU Cooling
When it comes to keeping your CPU cool, a heatsink plays a crucial role. But what exactly does it do? heatsink works hand in hand with other cooling components to maintain optimal CPU temperatures.
Heat Transfer Methods: Conduction and Convection
To understand how a heatsink cools the CPU, we need to grasp two important heat transfer methods: conduction and convection.
- Conduction: The heatsink comes into direct contact with the CPU, enabling heat transfer through conduction. The metal material of the heatsink quickly absorbs the heat from the CPU and spreads it across its surface, allowing it to dissipate efficiently.
- Convection: The fins on the heatsink play a vital role in facilitating heat dissipation through convection. As the heated air rises, cooler air from the surroundings replaces it, creating a continuous flow of air over the heatsink. This airflow carries away the heat, effectively cooling the CPU.
The Importance of Thermal Paste
To ensure optimal heat transfer between the CPU and the heatsink, thermal paste is applied. This paste fills in microscopic gaps and imperfections between the CPU and the heatsink, improving thermal conductivity. Without thermal paste, air gaps could form, hindering heat transfer and leading to higher CPU temperatures.
Risks of Running a CPU Without a Heatsink
Curious about what could go wrong if you decide to run your CPU without a heatsink? Well, it’s a risky move that can have serious consequences. The potential dangers and risks associated with running a CPU without proper cooling.
Potential Dangers of Running a CPU Without a Heatsink
Running a CPU without a heatsink can lead to a host of problems. The primary concern is the excessive heat generated by the CPU during operation. Without a heatsink to dissipate this heat, the CPU can quickly reach high temperatures, putting it at risk.
Impact on CPU Performance and Lifespan
Excessive heat negatively affects both the performance and lifespan of your CPU. When the CPU gets too hot, it can experience thermal throttling, a mechanism that slows down the CPU’s clock speed to reduce heat generation. This throttling can significantly impact performance, leading to slower and less responsive computing.
Moreover, prolonged exposure to high temperatures can shorten the lifespan of your CPU. Excessive heat can cause the delicate internal components of the CPU to degrade faster, potentially leading to permanent damage.
Thermal Throttling and Potential Damage
Thermal throttling, as mentioned earlier, is not only a performance concern but also an indication of potential damage to the CPU. It’s a protective measure implemented by the CPU to prevent overheating. However, if thermal throttling is frequently triggered due to inadequate cooling, it can strain the CPU and increase the risk of long-term damage.
Additionally, without a heatsink, the CPU is more prone to sudden temperature spikes, which can cause it to shut down unexpectedly. This can result in the loss of unsaved work and potential damage to the operating system.
Factors Affecting CPU Heat Dissipation
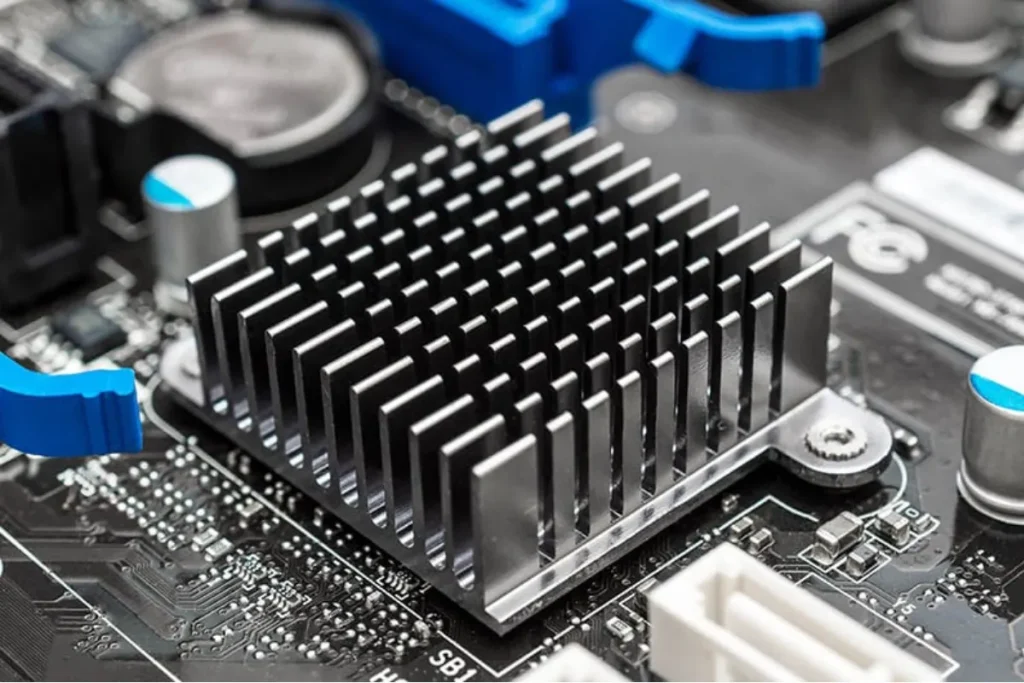
Ever wondered why some CPUs run hotter than others? Well, there are several factors that influence CPU heat dissipation. these factors, including CPU architecture, clock speed, workload intensity, and the impact of overclocking on CPU temperature.
CPU Architecture and Heat Dissipation
The architecture of a CPU plays a significant role in heat dissipation. Different CPU architectures have varying levels of power efficiency and thermal characteristics.
Modern architectures, such as those using smaller nanometer processes, tend to generate less heat compared to older ones. Additionally, advancements in microarchitecture design have led to improved heat management within the CPU.
Clock Speed and Heat Generation
The clock speed of a CPU, measured in gigahertz (GHz), determines how fast the CPU can process instructions.
Higher clock speeds often result in increased heat generation. As the CPU operates at higher frequencies, more electrical power is consumed, leading to greater heat production. This is why CPUs with higher clock speeds typically require more robust cooling solutions.
Workload Intensity and Heat Output
The intensity of the workload running on a CPU directly affects the heat output. CPU-intensive tasks, such as gaming or video rendering, put a significant load on the CPU, causing it to generate more heat.
On the other hand, less demanding tasks, like web browsing or word processing, produce lower heat levels. It’s important to consider the nature of your workload when assessing cooling requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are some tips for maintaining optimal CPU temperatures?
Ensure proper airflow in your computer case, regularly clean dust and debris, apply high-quality thermal paste, and monitor temperatures using software utilities.
2. How do I choose the right cooling solution for my CPU?
Consider factors like CPU power and heat output, available space in your case, noise preferences, and budget. Heatsinks with fans, liquid cooling systems, and fan configurations are common options.
3. Are liquid cooling systems better than traditional heatsinks and fans?
Liquid cooling systems offer excellent cooling performance and are generally more efficient. However, they can be more expensive, require additional maintenance, and may have a higher risk of leaks.
4. How often should I clean my CPU and cooling components?
It’s recommended to clean your CPU and cooling components every 3-6 months. However, the frequency may vary depending on factors like the environment and dust accumulation.
5. Can heat buildup damage my CPU?
Yes, excessive heat buildup can damage your CPU. High temperatures can degrade the CPU’s internal components, reduce performance, and potentially lead to system instability or failure.
Conclusion
Running a CPU without a heatsink is like running a marathon without shoes – it’s a risky business. Without a heatsink, the CPU can quickly overheat, leading to performance issues, instability, and potential damage. So, always make sure to use a proper heatsink to keep your CPU cool



